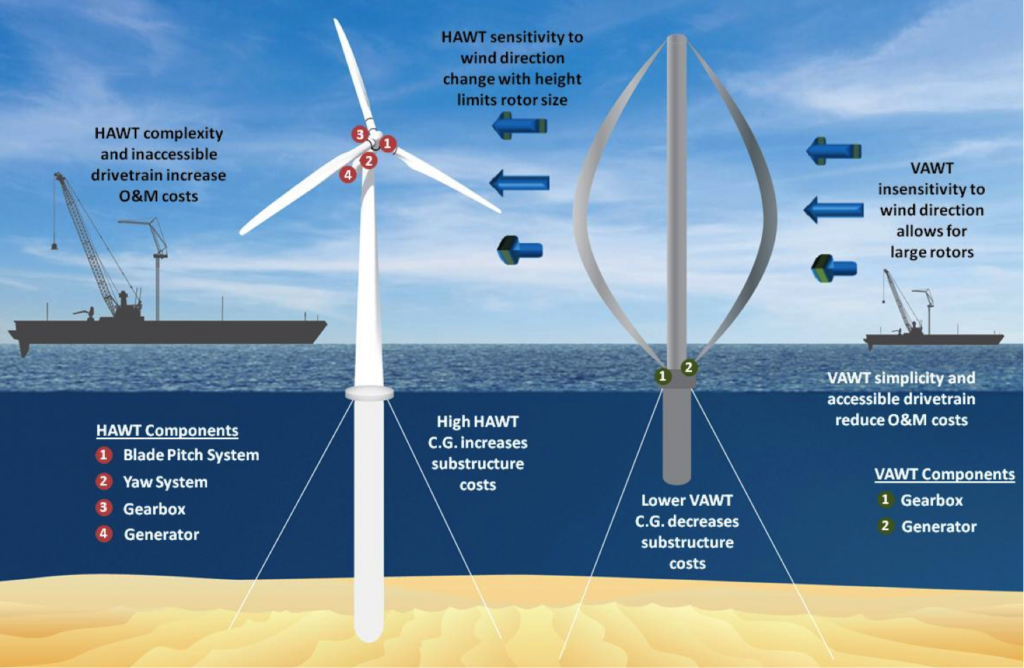
In the quest for sustainable and eco-friendly energy sources, vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWTs) have emerged as a promising solution. These innovative devices are changing the landscape of renewable energy production, offering unique advantages over their horizontal-axis counterparts. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the world of VAWTs, exploring their design, benefits, environmental impact, and their potential to revolutionize the way we harness the power of the wind.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Introduction
- Understanding Wind Energy
- The Basics of Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines
- 3.1. How VAWTs Differ from HAWTs
- 3.2. VAWT Designs
- Advantages of Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines
- 4.1. Improved Efficiency
- 4.2. Lower Noise Levels
- 4.3. Durability and Reliability
- Environmental Impact
- 5.1. Bird and Bat Friendliness
- 5.2. Aesthetics and Landscape
- Applications of VAWTs
- 6.1. Urban Environments
- 6.2. Off-Grid Solutions
- Challenges and Limitations
- 7.1. Scaling Up
- 7.2. Variable Wind Speeds
- Innovations and Future Prospects
- Conclusion
INTRODUCTION
Wind energy has long been a beacon of hope in the renewable energy sector. As the world grapples with the consequences of climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels, harnessing the power of the wind has become a vital part of the solution. Vertical-axis wind turbines, often abbreviated as VAWTs, represent a groundbreaking shift in the way we capture and utilize wind energy.
UNDERSTANDING WIND ENERGY
Before we delve into the intricacies of VAWTs, let’s take a moment to understand the fundamentals of wind energy. Wind is a clean, abundant, and renewable resource that is created by the sun’s uneven heating of the Earth’s surface. This natural phenomenon sets the stage for wind turbines to come into play.
THE BASICS OF VERTICAL-AXIS WIND TURBINES
3.1. HOW VAWTS DIFFER FROM HAWTS
One of the key distinctions between VAWTs and their horizontal-axis counterparts (HAWTs) lies in their orientation. VAWTs, as the name suggests, have a vertical axis of rotation, while HAWTs have a horizontal axis. This fundamental difference in design has far-reaching implications for their performance and applications.
3.2. VAWT DESIGNS
Vertical-axis wind turbines come in various designs, each with its unique features and advantages. Common VAWT designs include the Darrieus, Savonius, and Giromill. These designs cater to different wind conditions and purposes, making VAWTs highly adaptable.
ADVANTAGES OF VERTICAL-AXIS WIND TURBINES
4.1. IMPROVED EFFICIENCY
VAWTs have shown great promise in terms of efficiency. Their ability to capture wind from any direction, coupled with their streamlined design, results in consistent energy production, even in turbulent winds.
4.2. LOWER NOISE LEVELS
Compared to their HAWT counterparts, VAWTs are quieter during operation. This makes them a more attractive option for residential areas and wildlife habitats.
4.3. DURABILITY AND RELIABILITY
VAWTs are known for their robust construction, requiring minimal maintenance. Their simplicity contributes to enhanced reliability and longevity.
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT
5.1. BIRD AND BAT FRIENDLINESS
One significant environmental benefit of VAWTs is their reduced impact on bird and bat populations. The slow-moving vertical blades are less likely to harm wildlife.
5.2. AESTHETICS AND LANDSCAPE
VAWTs often blend more seamlessly into the landscape due to their compact design and slower rotation. This makes them a preferred choice in scenic areas.
APPLICATIONS OF VAWTS
6.1. URBAN ENVIRONMENTS
The compact size and reduced noise of VAWTs make them ideal for urban settings. They can be integrated into existing infrastructure to power homes and businesses.
6.2. OFF-GRID SOLUTIONS
In remote areas with limited access to the grid, VAWTs offer a reliable source of off-grid power, making them a lifeline for communities in need.
CHALLENGES AND LIMITATIONS
7.1. SCALING UP
While VAWTs offer numerous advantages, scaling up their power output remains a challenge. Researchers are actively working to address this limitation.
7.2. VARIABLE WIND SPEEDS
The performance of VAWTs can be affected by variable wind speeds, requiring sophisticated control systems for optimal energy generation.
INNOVATIONS AND FUTURE PROSPECTS
As technology continues to advance, we can expect exciting innovations in VAWT design and performance. These developments may further solidify their role in the renewable energy landscape.
CONCLUSION
Vertical-axis wind turbines represent a promising shift in the world of renewable energy. Their unique design, environmental benefits, and versatile applications make them a compelling choice for a sustainable future. By harnessing the power of the wind more efficiently and with less impact on the environment, VAWTs are contributing to a greener tomorrow.
