INTRODUCTION
In a world that’s increasingly aware of the environmental challenges posed by traditional energy sources, the search for sustainable alternatives is more critical than ever. Passive Solar Technology, a concept rooted in harnessing the power of the sun for various applications, is emerging as a beacon of hope in the realm of sustainable energy. This article will delve into the fascinating world of Passive Solar Technology, exploring its principles, applications, benefits, and much more.
What is Passive Solar Technology?
Passive Solar Technology is a simple yet ingenious approach to harnessing the sun’s energy for heating, cooling, and lighting buildings. Unlike active solar systems that require mechanical devices like solar panels and pumps, passive solar systems rely on natural processes to collect, store, and distribute solar energy.
Understanding the Principles
To grasp the essence of Passive Solar Technology, it’s crucial to understand its core principles:
1. Solar Gain
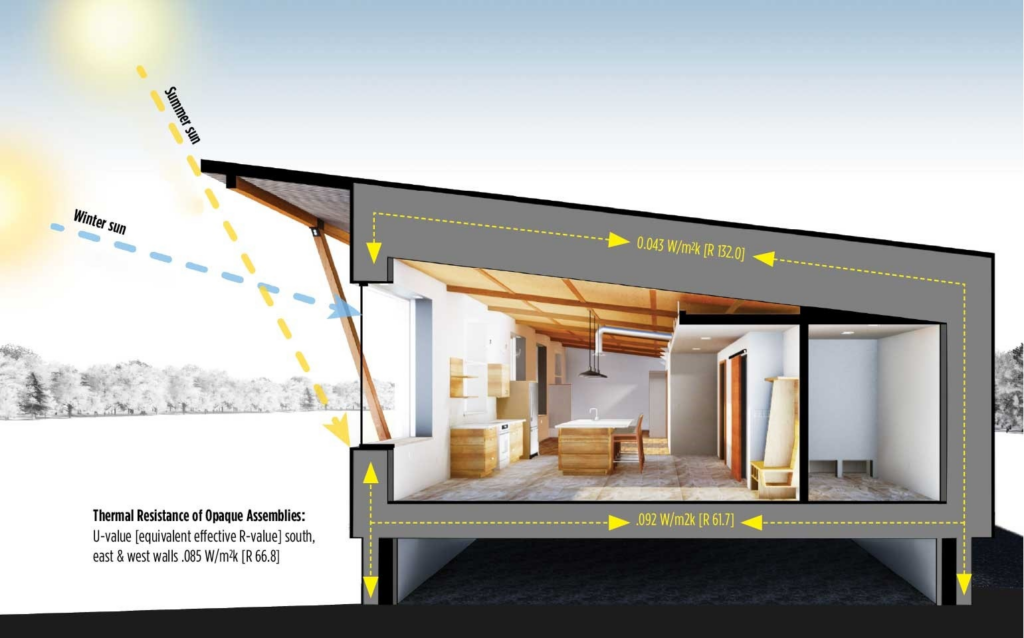
Solar gain, also known as solar heat gain or passive solar gain, is the process of capturing and utilizing solar radiation to heat a building. This is achieved through well-designed windows, thermal mass, and proper building orientation.
2. Thermal Mass
Thermal mass materials, such as concrete, stone, or water, absorb and store heat during the day and release it slowly during the night, regulating indoor temperatures.
Applications of Passive Solar Technology
Now that we’ve laid the foundation, let’s explore the diverse applications of Passive Solar Technology:
1. Solar Architecture
Passive Solar Technology plays a pivotal role in solar architecture. Architects design buildings with features like south-facing windows to maximize solar heat gain during the winter and minimize it during the summer.
2. Solar Water Heating
Solar water heaters use the sun’s energy to heat water for domestic use. These systems can significantly reduce energy bills and carbon footprints.
3. Daylighting
Harnessing natural light through strategically placed windows and skylights reduces the need for artificial lighting, enhancing energy efficiency.
4. Passive Solar Cooling
Passive cooling techniques, such as shading and ventilation, keep buildings comfortable in hot climates without relying on energy-intensive air conditioning.
The Advantages of Passive Solar Technology
The adoption of Passive Solar Technology offers a plethora of advantages:
1. Energy Efficiency
By reducing reliance on conventional heating and cooling systems, passive solar buildings are exceptionally energy-efficient, leading to lower utility bills.
2. Environmentally Friendly
Harnessing solar energy produces no greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a greener planet.
3. Cost-Effective
The initial investment in passive solar design and technology is offset by long-term savings on energy bills.
4. Comfort and Well-Being
Passive solar homes provide a more comfortable and naturally lit living environment, positively impacting occupants’ well-being.
Challenges and Considerations
While Passive Solar Technology offers immense promise, there are challenges and considerations to address:
1. Location
The effectiveness of passive solar systems depends on geographical location and climate conditions.
2. Initial Costs
Implementing passive solar features during construction can increase initial building costs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Passive Solar Technology represents a shining example of sustainable and eco-friendly energy solutions. Its ability to harness the power of the sun in ingenious ways not only benefits the environment but also offers financial advantages to homeowners. As we continue to grapple with the effects of climate change, embracing Passive Solar Technology may well be a giant leap toward a brighter, more sustainable future