Introduction
In a world where scientific advancements continue to push boundaries, the field of genetics has made remarkable strides. One such innovation that has captivated both the scientific community and the public is transgenics. This article aims to shed light on this cutting-edge topic, delving into its intricacies, applications, and ethical considerations.
What is Transgenics?
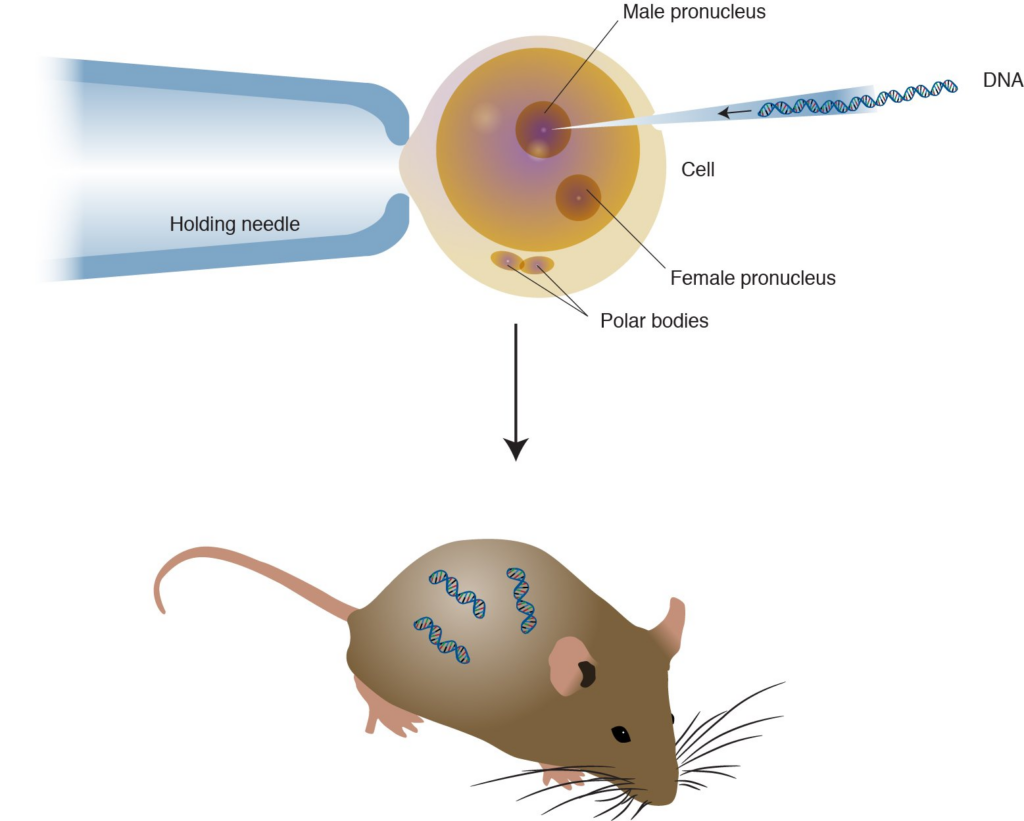
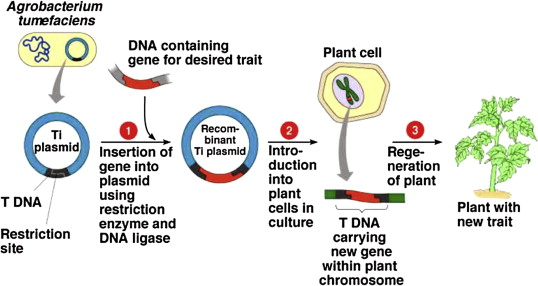
Transgenics is a revolutionary branch of genetic engineering that involves the transfer of genes from one species into another. These genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are created by introducing foreign DNA into the genetic code of an organism. This genetic manipulation allows for the expression of desired traits or the production of specific proteins.
THE GENESIS OF TRANSGENICS
A Brief History
The concept of manipulating genes dates back to the 1970s when scientists first attempted gene transfer experiments. However, it wasn’t until the 1980s that transgenic organisms were successfully created, marking a pivotal moment in genetic engineering.
The Mechanism
Transgenics relies on the precise manipulation of DNA. Scientists isolate the target gene, modify it as needed, and then insert it into the host organism’s genome using various techniques like microinjection or gene gun delivery.
APPLICATIONS OF TRANSGENICS
Transgenics has found applications in various fields, revolutionizing the way we approach challenges and opportunities.
Agriculture
Transgenic crops, such as genetically modified corn and soybeans, have become staples in modern agriculture. These crops are engineered to resist pests, tolerate herbicides, and even enhance their nutritional content.
Medicine
In the realm of medicine, transgenics has paved the way for the production of vital pharmaceuticals. Genetically modified bacteria and animals are used to produce insulin, growth hormones, and clotting factors.
Conservation
Transgenics plays a crucial role in conservation efforts. Scientists are developing transgenic species to combat extinction by enhancing their ability to survive in changing environments.
ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS
As with any groundbreaking technology, transgenics raises ethical questions and concerns.
Environmental Impact
Critics argue that genetically modified organisms may disrupt natural ecosystems or harm non-target species. Careful consideration of ecological consequences is essential.
Human Health
The safety of consuming GMOs is a topic of ongoing debate. Researchers continuously assess the long-term effects of genetically modified foods on human health.
CONCLUSION
Transgenics represents a remarkable fusion of science and technology. It has the potential to address critical challenges in agriculture, medicine, and conservation while raising important ethical questions. As we continue to unlock the secrets of genetics, responsible and informed decision-making will be crucial to harnessing the full potential of transgenic organisms.